SpringBoot源码分析之启动过程[1]
Spring Boot版本:2.1.8.RELEASE
Spring Boot启动过程是Spring Boot源码分析的第一章,其也是面试过程中Spring Boot方面考察较多的知识点之一。
从何入手
要分析Spring Boot的启动过程,需要从Spring Boot启动类的main函数入手:
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootAnalyzeApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootAnalyzeApplication.class, args);
}
}通过Java方法使用SpringApplication类来引导和启动Spring应用程序。
通过SpringApplication.run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) new一个SpringApplication实例,并调用其run方法。
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
// step1:new SpringApplication
// step2:springApplicaiton.run()
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}Step1:执行SpringApplication构造函数
SpringApplication构造函数主要执行以下步骤:
- 判断应用程序的类型
- 设置初始化器
- 设置监听器
- 找到项目的主类
new关键字调用SpringApplication的构造函数如下:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// 要使用的资源加载器,在上面的main函数中并没有传,因此为null
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 主要的bean资源,其实就是在main函数中传进去的SpringbootAnalyzeApplication类,即项目启动类
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 1.通过classpath中导入的jar包,判断应用程序的类型,有servlet/reactive/none类型
// 当我们引入spring-boot-starter-web,就是servlet类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 2.读取spring.factories文件中要载入的初始化器,并实例化
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 3.读取spring.factories文件中要载入的监听器,并实例化
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 4.找到项目的主类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}通过setInitializers和setListeners函数,Spring Boot从spring.factories文件中设置了如下实例:
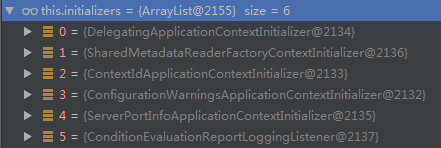
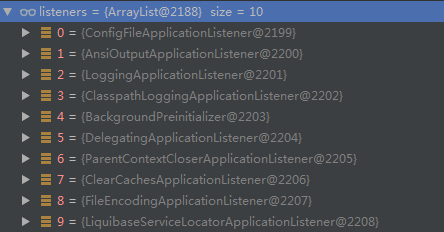
Step2:执行SpringApplication类的实例方法run()
首先介绍run方法中使用的SpringApplicationRunListeners对象
SpringApplicationRunListeners类中包含一个SpringApplicationRunListener类型的链表,链表中存储了Spring Boot的SpringApplicationRunListener对象。
SpringApplicationRunListener是SpringApplication的run方法的监听器。
SpringApplicationRunListener用来发布SpringApplicationEventSpring应用程序事件。
所谓的发布事件其实就是调用事件对应的监听器的onApplicationEvent方法。
每个事件对应唯一一个监听器,使用for循环遍历所有监听器,从而找到对应事件的监听器。
EventPublishingRunListener是SpringApplicationRunListener唯一的实现类。
run方法的执行步骤和对应阶段发布的事件:
- 应用程序开始准备:ApplicationStartingEvent
- 环境配置:ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
- 创建容器
- 准备容器:ApplicationContextInitializedEvent和ApplicationPreparedEvent
- 刷新容器:ContextRefreshedEvent和ServletWebServerInitializedEvent
- 应用程序准备完成:ApplicationReadyEvent
context:应用程序容器
environment:应用程序环境
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 构造一个秒表,用作记录
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 创建SpringApplicationRunListeners对象
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 1.start:广播ApplicationStartingEvent事件
listeners.starting();
try {
// main函数带的参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 2.环境配置:广播ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 3.根据程序的类型创建应用程序容器:servlet/reactive/none
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 4.准备容器
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 5.刷新容器
// 发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件
// 发布ServletWebServerInitializedEvent事件
refreshContext(context);
// 预留函数,方法体为空
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 6.running:发布ApplicationReadyEvent事件
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}涉及的主要函数
prepareEnvironment:准备环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
// 直接得到环境或者根据应用程序的类型创建一个环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}createApplicationContext:创建应用程序容器
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
// 根据应用程序的类型选择不一样的容器
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, " + "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}prepareContext:准备容器
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 设置容器环境
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 应用初始化器:for循环调用所有初始化器的initialize方法
applyInitializers(context);
// contextPrepared:广播ApplicationContextInitializedEvent事件
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
// contextLoaded:广播ApplicationPreparedEvent事件
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}refresh:刷新容器核心方法
在启动过程中不详细分析这部分代码,在之后的系列中会专门分析bean的加载过程。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 完成bean的实例化,包括开发人员在项目中自定义的bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}总结
Spring Boot项目的启动入口是项目启动类的main方法。通过main方法中的SpringApplication.run(SpringbootAnalyzeApplication.class, args);,Spring Boot项目实例化了一个SpringApplication对象,然后调用了这个对象的实例方法run()完成项目的启动。
因此对于项目的启动过程大致可以分为两块:
- 新建SpringApplication对象,执行构造方法里的语句。
- 执行SpringApplication对象的run实例方法。
执行SpringApplication的构造方法
- 判断应用程序的类型(reactive/servlet/none)
- 设置初始化器(初始化器用于应用程序的初始化)
- 设置监听器(监听器用于监听容器构建过程中发布的事件)
- 设置应用程序的主类
执行SpringApplication的run方法
应用程序开始准备:发布ApplicationStartingEvent事件
环境配置:
获取或根据应用程序类型创建默认环境。
发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件。
创建容器:根据应用程序类型创建默认容器
准备容器:
设置容器环境
应用初始化器
发布ApplicationContextInitializedEvent事件
设置容器的beanFactory和source
发布ApplicationPreparedEvent事件
刷新容器:
- 加载所有预置及自定义的bean,实例化bean的单例,等等
- 发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件
- 发布ServletWebServerInitializedEvent事件
应用程序准备完成:发布ApplicationReadyEvent事件
Spring Boot项目启动过程中,Bean单例的实例化等等操作是在刷新容器中做的,为了保证文章的可读性,作者将这部分从启动过程中剥离,将单独作为一章来分析。
附录
初始化器接口:包含
void initialize(C applicationContext)方法public interface ApplicationContextInitializer<C extends ConfigurableApplicationContext> { /** * Initialize the given application context. * @param applicationContext the application to configure */ void initialize(C applicationContext); }监听器接口:包含
void onApplicationEvent(E event)方法SpringApplicationRunListeners发布的事件最终会调用到对应监听器的onApplicationEvent方法
@FunctionalInterface public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener { /** * Handle an application event. * @param event the event to respond to */ void onApplicationEvent(E event); }EventPublishingRunListener类:监控run方法的执行
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered { private final SpringApplication application; private final String[] args; private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster; public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) { this.application = application; this.args = args; this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(); for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) { this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener); } } @Override public int getOrder() { return 0; } @Override public void starting() { this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args)); } @Override public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { this.initialMulticaster .multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment)); } @Override public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { this.initialMulticaster .multicastEvent(new ApplicationContextInitializedEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); } @Override public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.application.getListeners()) { if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware) { ((ApplicationContextAware) listener).setApplicationContext(context); } context.addApplicationListener(listener); } this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); } @Override public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { context.publishEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); } @Override public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { context.publishEvent(new ApplicationReadyEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); } @Override public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { ApplicationFailedEvent event = new ApplicationFailedEvent(this.application, this.args, context, exception); if (context != null && context.isActive()) { // Listeners have been registered to the application context so we should // use it at this point if we can context.publishEvent(event); } else { // An inactive context may not have a multicaster so we use our multicaster to // call all of the context's listeners instead if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) { for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : ((AbstractApplicationContext) context) .getApplicationListeners()) { this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener); } } this.initialMulticaster.setErrorHandler(new LoggingErrorHandler()); this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event); } } private static class LoggingErrorHandler implements ErrorHandler { private static Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(EventPublishingRunListener.class); @Override public void handleError(Throwable throwable) { logger.warn("Error calling ApplicationEventListener", throwable); } } }
转载请注明来源,欢迎对文章中的引用来源进行考证,欢迎指出任何有错误或不够清晰的表达。可以在下面评论区评论,也可以邮件至 504537531@qq.com
文章标题:SpringBoot源码分析之启动过程[1]
文章字数:2.2k
本文作者:YF
发布时间:2019-09-23, 16:23:14
最后更新:2019-10-15, 17:08:30
原始链接:https://zhouyufan0568.github.io/2019/09/23/springboot-startup-analysis/版权声明: "署名-非商用-相同方式共享 4.0" 转载请保留原文链接及作者。